shows a HART slave using DS8500 circuitry and the top-level blocks necessary f
or an
intelligent process transmit
ter. A temperature process transmitter serves as an example for this circuit. The sensor on the process transmitter measures the system temperature in current or voltage and then passes the data to the
ADC. The
ADC, in turn, converts these
analog signals to digital equivalents for the m
icrocontroller to process. The microcontroller provides remote memory along with computa
tion power. The microcontroller typically hosts the HART st
ack and is responsible for the protocol implementation; it also processes the digital data from the HART modem. Microcontroller capabilities
can also be used for sensor calibration,
linearization and signal conditioning. The
DAC is primarily responsible for driving the current loop.
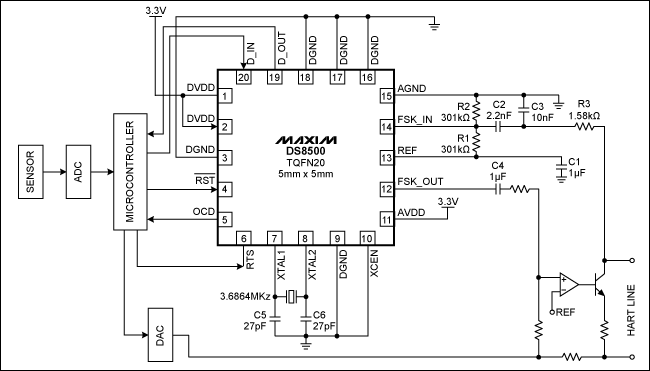
Figure 7. DS8500 on the slave side of HART communication. D_IN receives data from the microcontroller's
UART. D_OUT transmits data to the UART. Active-low
RST is the
DS8500 reset. OCD is a carrier-detect signal that determines a FSK signal with a valid amplitude at the input of the demodulator.
